The Group embraces a risk-aware culture and believes that an ingrained risk culture is the key to effective risk management, while training is a useful tool to promote and engage management and employees in ERM implementation. The Group promotes the risk culture with the following key themes:
The Group's ERM Framework aims to enhance the ability to achieve our vision and mission, and fulfil the five core values. In support of this, the Group has established a robust ERM framework with the following risk management objectives:
Risk appetite is defined to establish the extent and nature of risks the Group is willing to take in achieving our vision and mission. The Group’s risk appetite statement is disseminated across the Group and incorporated into our risk assessment criteria in order to align with our business objectives, core values, strategy, as well as risk management activities. The risk appetite statement is reviewed by the Board periodically to keep abreast of the ever-changing business environment and the latest development of the Group. The Group’s risk appetite is as follows:
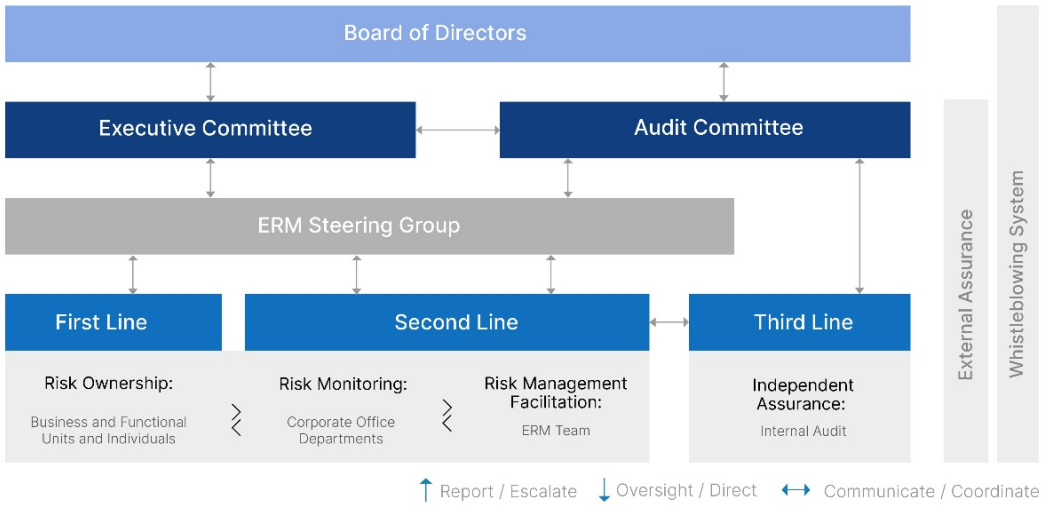
The overall risk management process is overseen by the Board. With the emphasis on value creation and protection, the Group adopts the Three Lines Model as its risk governance structure. The model clearly defines the responsibilities with enhancing collaboration and communication among different roles, which facilitates alignment of risk management activities and provides assurance to the Board.
Risk management process starts from the establishment of context, by taking into the consideration of the external environment and megatrends, as well as risk universe of the Group. Risks are then identified, analyzed, evaluated and treated with measures. With constant review, monitoring, reporting and consultation, the risk management process integrates with various business processes and activities in optimizing the risk and return.
To facilitate a comprehensive and robust risk management process, top-down and bottom-up approaches are employed to gather risk insights as well as to monitor and manage risks from the perspectives of both sides, together with “ERM Policy” and “ERM Manual” to provide proper guidance. Also, interactive communication between the risk owners and the ERM Team is in place to enable both parties to keep abreast of risk updates.
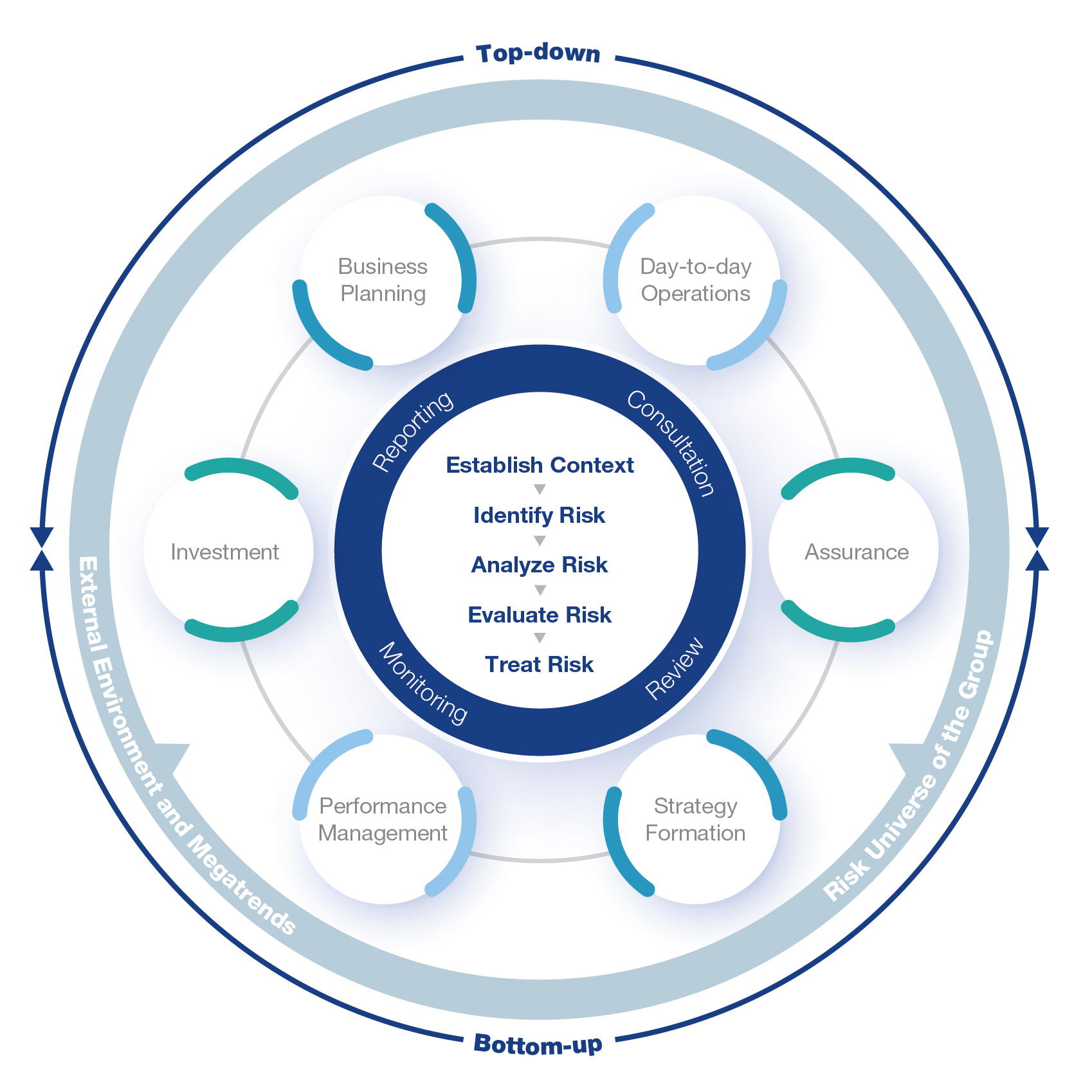
1. Establishment of Context
The Group defines the internal and external contexts as well as the parameters for risk assessment criteria.
2. Risk Identification
The Group adopts both Top-down and Bottom-up approaches, complemented with Outside-in and Spread-out mechanisms to facilitate a comprehensive risk identification process.

3. Risk Analysis
Business and functional units and corporate office departments assess the likelihood, impact, risk velocity, inherent risk level and residual risk level of the key risks identified.
4. Risk Evaluation
The risk analysis results are compared with the risk appetite and tolerance level. This allows management to determine the risk response strategy for each risk and prioritize risk treatment plans.
5. Risk Treatment
Risk treatment plans for implementing risk mitigation measures are developed by respective business and functional units and corporate office departments, based on the priority and nature of risks.
Continual tracking, review and validation of the implementation of our ERM framework have been in place to monitor various risks, change in risk exposure, their residual risk levels, as well as to ensure and increase the effectiveness and quality of ERM framework and outcomes.
Risk Register
Business and functional units and corporate office departments perform self-assessment of the effectiveness of the risk treatment plans upon the submission of the Risk Register every half year.
Key Risk Indicator
KRIs are set by risk owners to measure and monitor changes in risk exposure of key risks. If there is any KRI value exceeding the pre-defined threshold, risk alerts to management will be mandated so that they can timely administer corresponding responses, and proper reporting to Executive Directors will be made.
Risk Treatment Validation
The ERM Team reviews the implementation and effectiveness of risk mitigation measures stated in the Risk Register. The Internal Audit Team also performs risk-based validation to test risk mitigation measures of key risks during the internal audit process.
Early Risk Flagging Mechanism
An early risk flagging mechanism is applied across the Group, to proactively identify and assess emerging risks and risks with high velocity, such as quality, health and safety, disaster and media events. When a potential risk is perceived with significant impact, the risk should be flagged and reported to line manager and risk oversight parties.
Whistleblowing Mechanism
The Group has established a whistleblowing policy and provided reporting channels for internal and external stakeholders. Whistleblowing cases are reported to the Executive Committee and the Audit Committee. For details, please refer to the Corporate Governance Report of the annual report.
Review on the Effectiveness of Risk Management and Internal Control Systems
The Board, with the assistance from the Audit Committee, Corporate Governance Committee and Sustainability Committee, reviewed and evaluated the effectiveness of the Group’s risk management and internal control systems (including ESG risks and climate-related risks), including the consideration of the following factors:
In addition to the above, the Integrated Internal Control Self-Assessment Certificate is applied across the Group to evaluate the effectiveness of its risk management and internal control systems semi-annually by business and functional units and corporate office departments, with reference to the COSO framework. Regarding the review of the effectiveness of the risk management and internal control systems and its results, please refer to the Corporate Governance Report for details.
Regular reporting, regarding identified risks and the status of risk management activities, is provided to management, the ERM Steering Group, the Executive Committee and the Audit Committee to facilitate the risk management process and decision-making. The ERM Steering Group Meeting is held every half year to discuss key risk matters and updates.
ERM is embedded into decision-making and business processes, including but not limited to the following key organizational processes:
Business Planning
Potential risks, which may impact the achievement of business objectives, are identified and considered in strategic planning, and project and operational plans. This could better align business strategy and process with the risk appetite set at the early stage.
Investment
Investment proposals are reviewed with the consideration of risks (including ESG risks and climate-related risks) before decision-making. Feasibility study and/ or due diligence are conducted to identify and assess potential risks and relevant costs for risk treatment. Review and reporting processes are in place to analyze and monitor the change of risks throughout the investment management cycle. Response strategy is formulated and executed timely to address any material changes of risk exposure of an investment project.
Day-to-day Operations
The Group establishes a framework for business and functional units and corporate office departments to understand and evaluate their risk profiles and exposures (including ESG risks and climate-related risks) systematically. Risk treatment plans designed during the ERM process have been incorporated in their operational plans and implemented with regular monitoring. KRI mechanism is applied to detect abnormal changes to risk exposures for timely escalation and treatment.
The Group invests and operates a wide range of businesses predominantly in Hong Kong and the Mainland. Our businesses include toll roads, construction, insurance, logistics, and facilities management.
Through the comprehensive risk management process mentioned in the previous section, the Group identified major risks which may affect the achievement of the Group’s business objectives. However, risk evolves from the interactions of many dynamic forces and factors in the business environment. Some risks are not significant now but could become key ones in the future; certain risks exist but we are not aware of; and/or new risks come to light. Therefore, our risk portfolio would be reviewed and updated to react and respond to the changing risk landscape.
As the pandemic gradually recedes, its impact on our operation has been much less significant and the business has transitioned back to normalcy. While it no longer remains our primary concern, we stay attentive to any potential hazards that could unexpectedly arise and develop into immediate challenges.
In the post-pandemic era, market competition has become intense as businesses strive to regain lost ground. We pay close attention to the competition and remain committed to refining strategies, optimizing efficiency, and fostering innovation to maintain a competitive edge.
Corporations does not only compete for customers, but talents. Talent competition has been a hot topic as economic activities steadily recover together with the shrinking talent pool. This trend has become particularly evident following the implementation of enhanced talent attraction policies in different cities and countries. Therefore, effective talent attraction and retention strategies have been our top priority so as to support business development.
During the year, the macroeconomic environment remains relatively unstable due to concerns about surging inflation and interest rates, fluctuating exchange rates, and economic downturn. Throughout the years, we have been vigilant in navigating these conditions and capitalizing on emerging opportunities by implementing strategic and financial initiatives such as the disposal of commercial aircraft leasing platform and issuance of Panda Bonds to strengthen our financial position.
Meanwhile, geopolitical risk has been an increasing attention to the Group due to the geopolitical conflicts including the China-United States tensions, cross-Strait relations, and Russo-Ukrainian War during the year. Since the shock arising from those conflicts could be tremendous, we keep a close eye on the development of various geopolitical issues including but not limited to new restrictive policies, sanctions, tariffs and military conflicts for the purpose of timely and appropriate reaction and mitigation measures.
Aside from geopolitical risk, climate change and sustainability risks continue to be major concerns for our business, as it has been amplifying the breadth and depth of the impact such as more frequent extreme weather events and tightening regulatory requirements. Consequently, we have continually increased our attention and efforts in managing these impacts on our business, the community and the planet.
The Group will keep monitoring and managing the uncertainties in achieving the business objectives.
Please refer to the following table of the major risks identified by the Group and the corresponding mitigation measures for the Group’s efforts in managing the major risk profile. The table below is neither intended to be exhaustive nor comprehensive.
Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures
Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures
Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures
Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures

Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures
Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures
Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures
Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures
Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures
Risk Description
Risk Trend

Mitigation Measures
ESG issues and climate change are widely recognized as key topics that all sectors need to address, as it could bring multi-faceted impacts to sustainable business growth and community development. The Group emphasizes the importance of ESG risks and climate-related risks, and therefore has integrated those risks into our ERM framework in order to facilitate the achievement of the NWS Sustainability Target 2030 and develop resilience for both physical and transition impacts under climate change.
The Board takes ultimate responsibility for ESG and sustainability of the Group, which oversees the Group’s ESG strategy and progress against respective goals and targets. With the delegation from the Board, the Audit Committee oversees ESG risks and climate-related risks, monitors uncertainty affecting the achievement of ESG goals and targets, and evaluates effectiveness of mitigations to manage the risks.
The Group applies the aforementioned risk management process, ranging from risk assessment and treatment to consultation and reporting, to the management of ESG risks and climate-related risks which have been incorporated with the Group’s risk profile, such as talent attraction and retention, regulatory compliance, environmental, sustainability governance, etc. Other than ordinary risks, ESG and climate-related topics are also our discussion focus during the risk identification exercise to obtain insights and form the basis of the Group’s risk profile, which is part of the regular reporting to the ERM Steering Group, Executive Committee and Audit Committee.
In considering the characteristics of ESG risks and climate-related risks, the Group has made some appropriate adjustments during the integration of those risks into the ERM framework. For instance, different time horizons have been used in the assessment criteria of climate-related risks. Since FY2019, the Group has undertaken multiple climate-related risk assessments and disclosure reviews with external consultants. For example, a few major assets have been selected for a physical risk assessment and the assessment approach serves as a blueprint for replicating and scaling similar initiatives across our business units. Furthermore, for systematic climate-related risk management and integration, a technical guide has been established to articulate the procedures for identification, assessment and management of climate-related transition risks. To stay abreast of the future uncertainties of climate change, the Group has also developed a net zero roadmap in preparation for the upcoming transition to net zero. For the details on ESG and climate-related risk management initiatives, please refer to the Corporate Governance Report and the Sustainability Report.
Additionally, to enhance the awareness and understanding of ESG risks and climate-related risks, we have organized webinars and training sessions periodically to share information and knowledge about emerging trends and popular ESG and climate-related topics with management, risk owners and relevant individuals. For example, during the year, we organized cyber security risk training webinar and workshop for our staff, management and the Board to enhance their cyber security awareness. Moreover, in the refresher training this year, climate-related risk trend and assessment approach were explained to the risk owners and reporting persons.